SystemC 06 Simulation Stages
The systemC application has three phases/stages of operation
-
Elaboration: execution of statements prior to
sc_start().- The primary purpose is to create internal data structures to support the semantics of simulation.
- During elaboration, the parts of the module hierarchy (modules, ports, primitive channels, and processes) are created, and ports and exports are bound to channels.
-
Execution: further break-down to two stages:
- a) Initialization
- simulation kernel identifies all simulation processes and place them in either a runnable or waiting process set.
- All simulation processes are in runnable set except those requesting “no initialization”.
- b) Simulation
- is commonly described as a state machine that schedules processes to run, and advances simulation time. It has two internal phases:
- 1) evaluate: run all runnable processes one at a time. Each process runs till reaches wait() or return. Stops if no runnable processes left.
- 2) advance-time: once the set of runnable processes is emptied, simulation enters advance-time phase where it does:
- a) move simulated time to the closest time with a scheduled event
- b) move processes waiting for that particular time into the runnable set
- c) return to evaluation phase
- The progression from evaluate to advance-time continues until one of the three things occurs. Then it moves to the cleanup phase.
- a) all processes have yielded
- b) a process has executed
sc_stop() - c) maximum time is reached
- is commonly described as a state machine that schedules processes to run, and advances simulation time. It has two internal phases:
- a) Initialization
- Cleanup or post-processing: destroy objects, releases memory, close open files etc.
Four callback functions
are called by the kernel at various stages during elaboration and simulation. They have the following declarations:
-
virtual void before_end_of_elaboration():- called after the construction of the module hierarchy
-
virtual void end_of_elaboration():- called at the very end of elaboration after all callbacks to
before_end_of_elaborationhave completed and after the completion of any instantiation or port binding performed by those callbacks and before starting simulation.
- called at the very end of elaboration after all callbacks to
-
virtual void start_of_simulation():- a) called immediately when the application calls
sc_startfor the first time or at the very start of simulation, if simulation is initiated under the direct control of the kernel. - b) if an application makes multiple calls to
sc_start, start_of_simulation is called on the first call tosc_start. - c) called after the callbacks to
end_of_elaborationand before invoking the initialization phase of the scheduler.
- a) called immediately when the application calls
-
virtual void end_of_simulation():- a) called when the scheduler halts because of
sc_stopor at the very end of simulation if simulation is initiated under the direct control of the kernel. - b) called only once even if
sc_stopis called multiple times.
- a) called when the scheduler halts because of
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
// Learn with Examples, 2020, MIT license
#include <systemc>
using namespace sc_core;
SC_MODULE(STAGE) {
SC_CTOR(STAGE) { // elaboration
std::cout << sc_time_stamp() << ": Elaboration: constructor" << std::endl;
SC_THREAD(thread); // initialization + simulation
}
~STAGE() { // cleanup
std::cout << sc_time_stamp() << ": Cleanup: desctructor" << std::endl;
}
void thread() {
std::cout << sc_time_stamp() << ": Execution.initialization" << std::endl;
int i = 0;
while(true) {
wait(1, SC_SEC); // advance-time
std::cout << sc_time_stamp() << ": Execution.simulation" << std::endl; // evaluation
if (++i >= 2) {
sc_stop(); // stop simulation after 2 iterations
}
}
}
void before_end_of_elaboration() {
std::cout << "before end of elaboration" << std::endl;
}
void end_of_elaboration() {
std::cout << "end of elaboration" << std::endl;
}
void start_of_simulation() {
std::cout << "start of simulation" << std::endl;
}
void end_of_simulation() {
std::cout << "end of simulation" << std::endl;
}
};
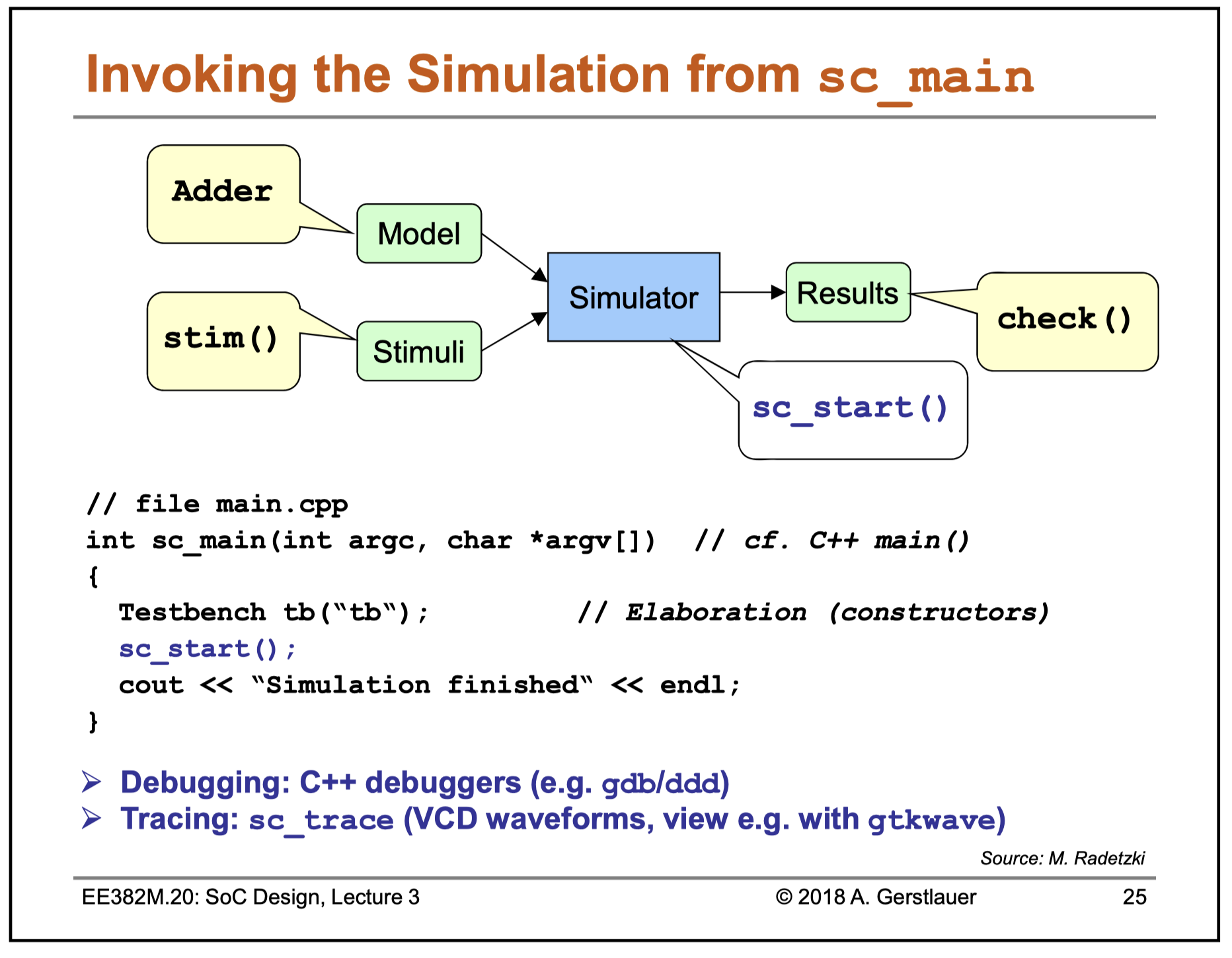
int sc_main(int, char*[]) {
STAGE stage("stage"); // Elaboration
sc_start(); // Execution till sc_stop
return 0; // Cleanup
}
//=
// Result
0 s: Elaboration: constructor
// callback: before_end_of_elaboration()
before end of elaboration
// callback: end_of_elaboration()
end of elaboration
// callback: start_of_simulation()
start of simulation
// initialization
0 s: Execution.initialization
// iteration #1
1 s: Execution.simulation
// iteration #2
2 s: Execution.simulation
// sc_stop triggered
Info: /OSCI/SystemC: Simulation stopped by user.
// callback: end_of_simulation
end of simulation
2 s: Cleanup: desctructor