SystemC 09 Event
Event
An event is an object of class sc_event used for process synchronization.
A process instance may be triggered or resumed on the occurrence of an event, i.e., when the event is notified.
Any given event may be notified on many separate occasions.
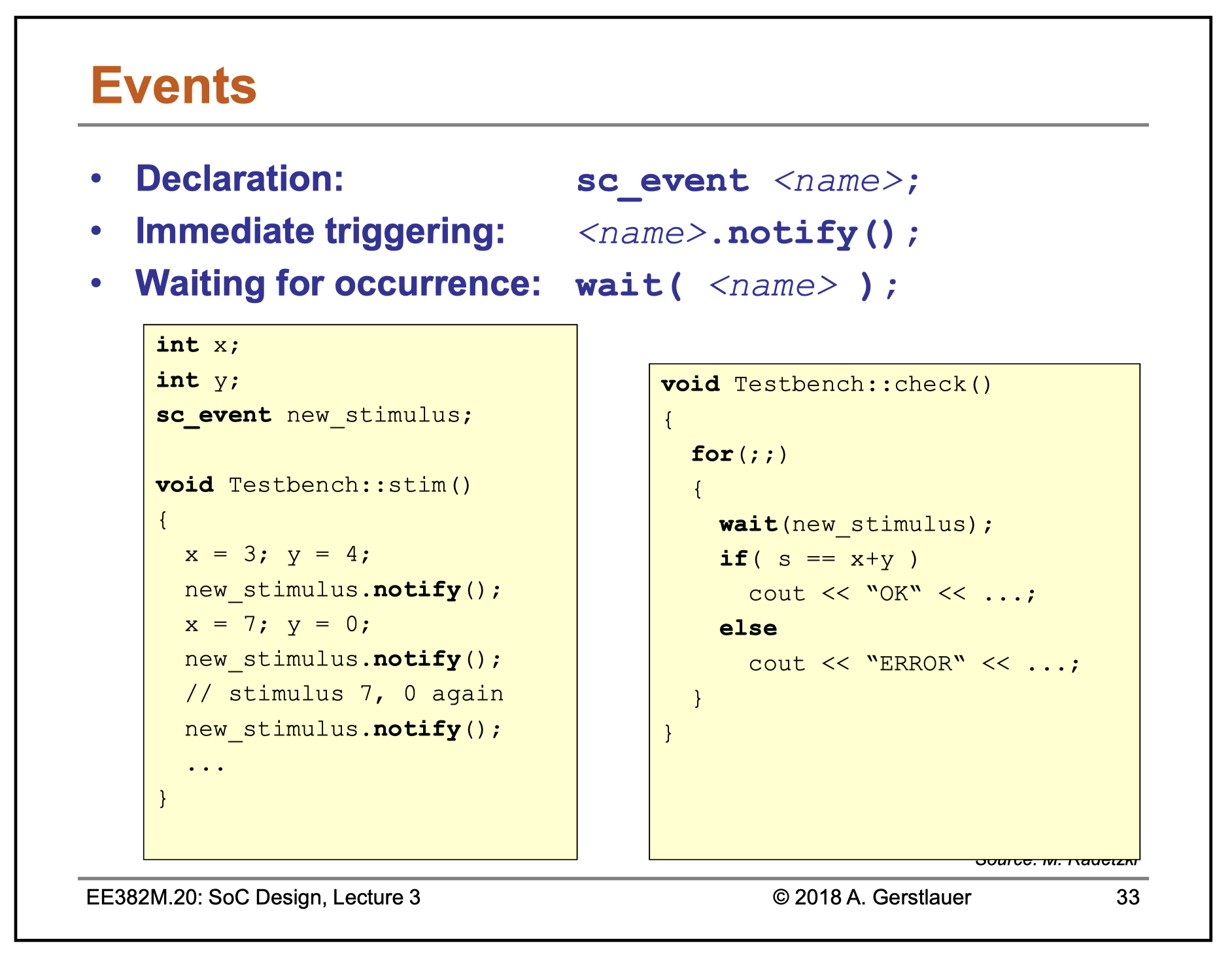
sc_event
has the following methods:
-
void notify(): create an immediate notification -
void notify(const sc_time&),void notify(double, sc_time_unit):- a) zero time: create a delta notification.
- b) non-zero time: create a timed notification at the given time, expressed relative to the simulation time when function notify is called
-
cancel(): delete any pending notification for this event- a) At most one pending notification can exist for any given event.
- b) Immediate notification cannot be cancelled.
Constraints on sc_event
- Objects of class
sc_eventmay be constructed during elaboration or simulation. - Events may be notified during elaboration or simulation, except that it shall be an error to create an immediate notification during elaboration or from one of the callbacks:
- a) before_end_of_elaboration,
- b) end_of_elaboration, or
- c) start_of_simulation.
No more than one pending notification
A given event shall have no more than one pending notification:
- If function notify is called for an event that already has a notification pending, only the notification scheduled to occur at the earliest time shall survive.
- The notification scheduled to occur at the later time shall be cancelled (or never be scheduled in the first place).
- An immediate notification is taken to occur earlier than a delta notification, and a delta notification earlier than a timed notification. This is irrespective of the order in which function notify is called.
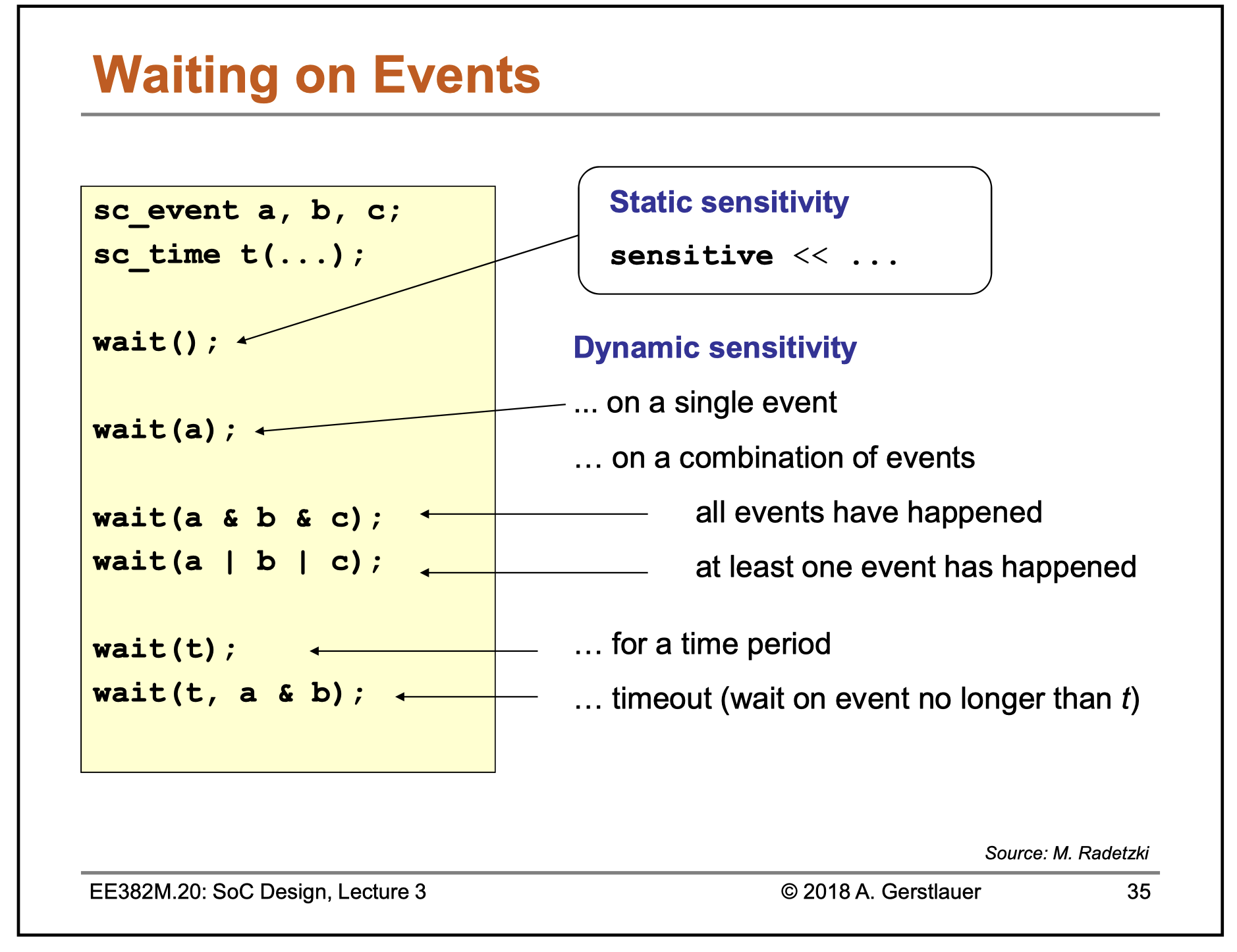
Events can be combined with each other, and with a timer. This example shows a process waiting for only one event.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// Learn with Examples, 2020, MIT license
#include <systemc>
using namespace sc_core;
SC_MODULE(EVENT) {
sc_event e; // declare an event
SC_CTOR(EVENT) {
SC_THREAD(trigger); //register a trigger process
SC_THREAD(catcher); // register a catcher process
}
void trigger() {
while (true) { // infinite loop
e.notify(1, SC_SEC); // trigger after 1 second
if (sc_time_stamp() == sc_time(4, SC_SEC)) {
e.cancel(); // cancel the event triggered at time = 4 s
}
wait(2, SC_SEC); // wait for 2 seconds before triggering again
}
}
void catcher() {
while (true) { // loop forever
wait(e); // wait for event
std::cout << "Event cateched at " << sc_time_stamp() << std::endl; // print to console
}
}
};
int sc_main(int, char*[]) {
EVENT event("event"); // define object
sc_start(8, SC_SEC); // run simulation for 8 seconds
return 0;
}
// Result
// trigged at 0 s
Event cateched at 1 s
// triggered at 2 s
Event cateched at 3 s
// the event triggered at 4 s is cancelled
// triggered at 6 s
Event cateched at 7 s