AlgoExpert 011-020
11. Depth-first Search

- Node 클래스에 있는
depthFirstSearch멤버함수는 -
vector<string> *array포인터를 받아서 현재 노드의 name에 적힌 값을push_back해주고, - 현재 노드 children의 각 원소인 child 포인터의
depthFirstSearch멤버함수를 재귀적으로 호출한다. - 모든 node는 array 포인터를 return 하지만, (코드에는 안 보이는) main 함수에서 쓰이는 root node에서만 호출되는거라 별 필요 없는 듯.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Do not edit the class below except
// for the depthFirstSearch method.
// Feel free to add new properties
// and methods to the class.
class Node {
public:
string name;
vector<Node *> children;
Node(string str) { name = str; }
vector<string> depthFirstSearch(vector<string> *array) {
// Write your code here.
array->push_back(name);
for (auto child: children){
child->depthFirstSearch(array);
}
return (*array);
}
Node *addChild(string name) {
Node *child = new Node(name);
children.push_back(child);
return this;
}
};
- 한줄요약: DFS 함수 시작하면 현재 노드 값을 array에 저장하고, children의 원소들마다 DFS 함수를 재귀적으로 호출해주자.
12. Minimum Waiting Time

용어 정의:
- 쿼리 실행 시간: queries 벡터의 integer 걊은 각 쿼리가 실행되는 시간
- Waiting time: 해당 쿼리가 앞에 있는 쿼리들이 실행되는 동안 기다려야하는 시간
- Total waiting time: 모든 쿼리의 waiting time을 구해서 더한 값
- Minimum waiting time:
- 가능한 쿼리의 순서 조합 가운데 가장 낮은 total waiting time
- 맨 앞에 큰 시간이 소요되면, 중복해서 뒤 쪽 쿼리의 waiting time에 더해짐
- 따라서 sorting 해서 적은 실행시간이 걸리는 쿼리부터 처리해주어야 minimum waiting time 구할 수 있음
- 먼저 queries vector를 sorting 해주고,
- 맨 앞 query의 waiting time = 0, execution time = queries[0]
- 그 다음 query의 waiting time = previous waiting time (0) + previous execution time (queries[0])
- 이걸 iteration하면 끝!
즉, 포인터가 벡터의 오른쪽으로 움직이면서, 이전 기록을 accumulate 해주는 변수를 따라서 업데이트 해주면 됨.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
using namespace std;
int minimumWaitingTime(vector<int> queries) {
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());
int prevDelay = 0;
int delay=0;
int sum =0;
for (int q : queries){
prevDelay = delay;
sum += delay;
delay += q;
cout << "q:" << q <<" prevDelay:" << prevDelay << " delay:" << delay << " sum:" << sum << endl;
}
// Write your code here.
return sum;
}
- 한줄요약: 벡터 sorting 한 다음에, iterate 해주면서 이전 단계의 execution time이용해서 현재 단계의 waiting time 업데이트하고 accumulate하기
13. Class Photos

사진 찍기 룰:
- 빨간 셔츠 학생끼리 줄 세우고, 파란 셔츠 학생끼리 줄을 세운 상태에서
- 뒷 줄 학생은 항상 앞 줄 학생보다 키가 커야함
이 룰 만족하는지 테스트해주는 함수 만들기
- 일단 redShirtHeights와 blueShirtHeights를 sorting해주자
- redShirtHeights와 redShirtHeights의 최댓값 (마지막 index =
redShirtHeights.size()-1) 을 비교해서 큰 쪽 학생들을 뒷줄에 세우고, - redShirtHeights와 모든 element (각 학생의 키)가 같은 index의 blueShirtHeights보다 큰지 (혹은 작은지) 테스트해서, false 를 return
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool classPhotos(vector<int> redShirtHeights, vector<int> blueShirtHeights) {
// Write your code here.
int end = redShirtHeights.size()-1;
sort(redShirtHeights.begin(),redShirtHeights.end());
sort(blueShirtHeights.begin(),blueShirtHeights.end());
if ( redShirtHeights[end] < blueShirtHeights[end] ) {
// red is front row
for (int i = end; i >= 0; i--){
if (redShirtHeights[i] >= blueShirtHeights[i]) return false;
}
}
else {
// blue is front row
for (int i = end; i >= 0; i--){
if (redShirtHeights[i] <= blueShirtHeights[i]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
- 한줄요약: 두 벡터 sorting해서 최댓값 비교하고, 모든 원소도 비교.
14. Tandem Bicycle


redShirtSpeeds 와 blueShirtSpeeds를 하나씩 짝 지어서 더 큰 스피드가 tandem bicycle의 스피드를 결정함. Total speed가 최대가 되게 하려면
- 각 벡터를 sort 하고
- 각 벡터의 맨 뒤에 있는 값끼리 비교해서, 큰 값을 sum에 더하고,
- 이긴쪽 포인터만 (진 쪽 벡터의 포인터는 그대로) 왼쪽으로 이동.
- 이걸 n번 (벡터의 크기)만큼 시행하면
- 결과적으로 두 벡터에서 큰 순서대로 n개의 스피드를 골라서 더하는 꼴이 됨.
- 선택되지 않은 값들은 자동적으로 선택된 값들에 매치되는 것으로 볼 수 있음
반대로 Total speed가 최소가 되게 하려면,
- 이긴쪽 포인터와 진 쪽 벡터의 포인터를 모두 왼쪽으로 이동.
- 이게 무슨 뜻이냐면, 두 벡터의 빠른 애들끼리 짝을 만들어서 tandem bicycle에 태우면, 진 쪽 스피드가 낭비되는 셈이라서 최소 total speed가 생김
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int maxSum (int n, vector<int>& redShirtSpeeds, vector<int>& blueShirtSpeeds){
int sum=0;
int j = n-1;
int k = n-1;
for (int i=0; i < n; i++ ){
if (redShirtSpeeds[j] >= blueShirtSpeeds[k]){
sum += redShirtSpeeds[j--];
}
else {
sum += blueShirtSpeeds[k--];
}
}
return sum;
}
int minSum (int n, vector<int>& redShirtSpeeds, vector<int>& blueShirtSpeeds){
int sum=0;
int j = n-1;
int k = n-1;
for (int i=0; i < n; i++ ){
if (redShirtSpeeds[j] >= blueShirtSpeeds[k]){
sum += redShirtSpeeds[j--];
k--;
}
else {
sum += blueShirtSpeeds[k--];
j--;
}
}
return sum;
}
int tandemBicycle(
vector<int> redShirtSpeeds, vector<int> blueShirtSpeeds, bool fastest
) {
// Write your code here.
int sum;
sort(redShirtSpeeds.begin(),redShirtSpeeds.end());
sort(blueShirtSpeeds.begin(),blueShirtSpeeds.end());
int n = blueShirtSpeeds.size();
if (fastest) sum = maxSum(n, redShirtSpeeds, blueShirtSpeeds);
else sum = minSum(n, redShirtSpeeds, blueShirtSpeeds);
return sum;
}
- 한줄요약: 크기 n인 두 벡터에서 n쌍을 만들어서 (1) max-speed-sum 만들 땐, 두 벡터에서 큰 값만 n개 고르고 (상대 쌍은 implicitly 작은 값들로 매치됨), min-speed-sum만들 땐 두 벡터에서 큰 것들끼리 n 쌍을 이루게 하자 (상대적으로 작은 큰 값은 speed-sum에 계수 안되서 낭비됨).
15. Optimal Freelancing

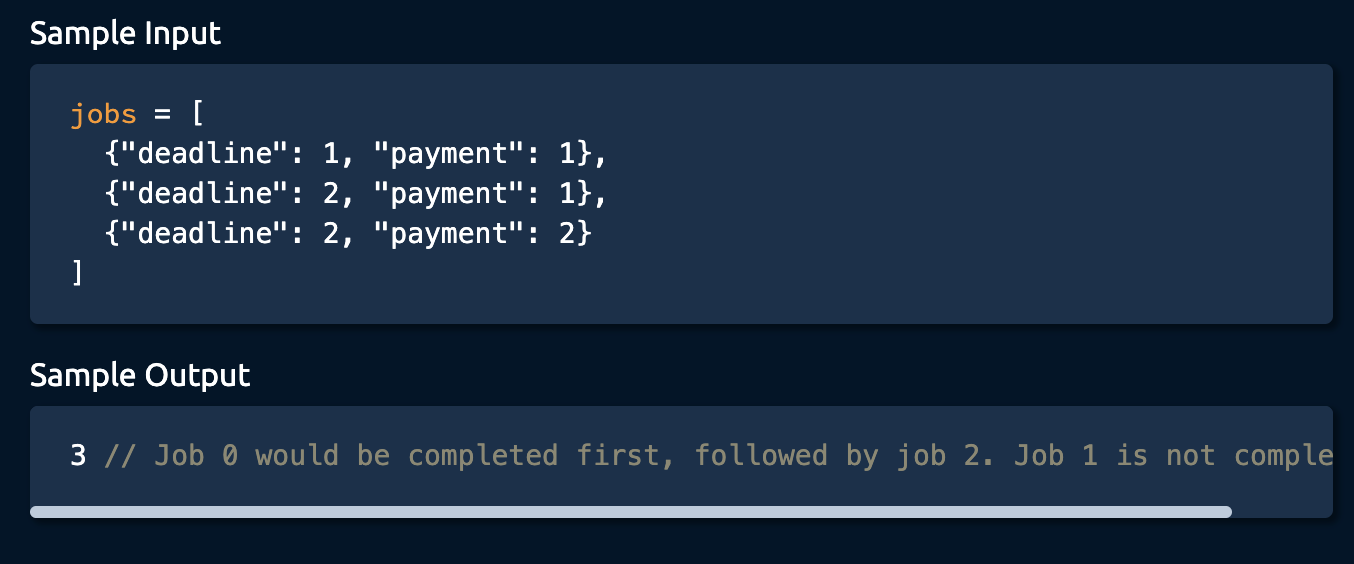
- Payment 순서대로 sorting
- lambda function 써서 “<” opertion을 오버로딩해줘야 함.
- 7 칸짜리 bool 벡터 timeline 만들고,
- for-loop에서 payment 큰 job 부터 timeline 채우자
- 선택된 job의 deadline에 해당하는 timeline 칸부터 시작해서
- 왼쪽으로 가면서 false, 즉 아직 job이 할당되지 않은 칸을 찾아서 true로 바꿔서 job이 할당 되었음을 표시하고,
- profit에 payment를 더한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
using namespace std;
int optimalFreelancing(vector<unordered_map<string, int>> jobs) {
// Write your code here.
// With Sort
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end(), [](unordered_map<string, int> a, unordered_map<string, int> b){
return a.find("payment")->second > b.find("payment")->second;
});
vector<bool> timeline(7, false);
int profit = 0;
for (auto &job : jobs){
int maxTime = min(job.at("deadline"),7);
for (int i = maxTime; i > 0 ; i--){
if(timeline[i]==false){
timeline[i] = true;
profit += job.at("payment");
break;
}
}
}
return profit;
}
-
한줄요약: 높은 payment 순으로 deadline에 최대한 가까운 날짜에 스케쥴하자!
-
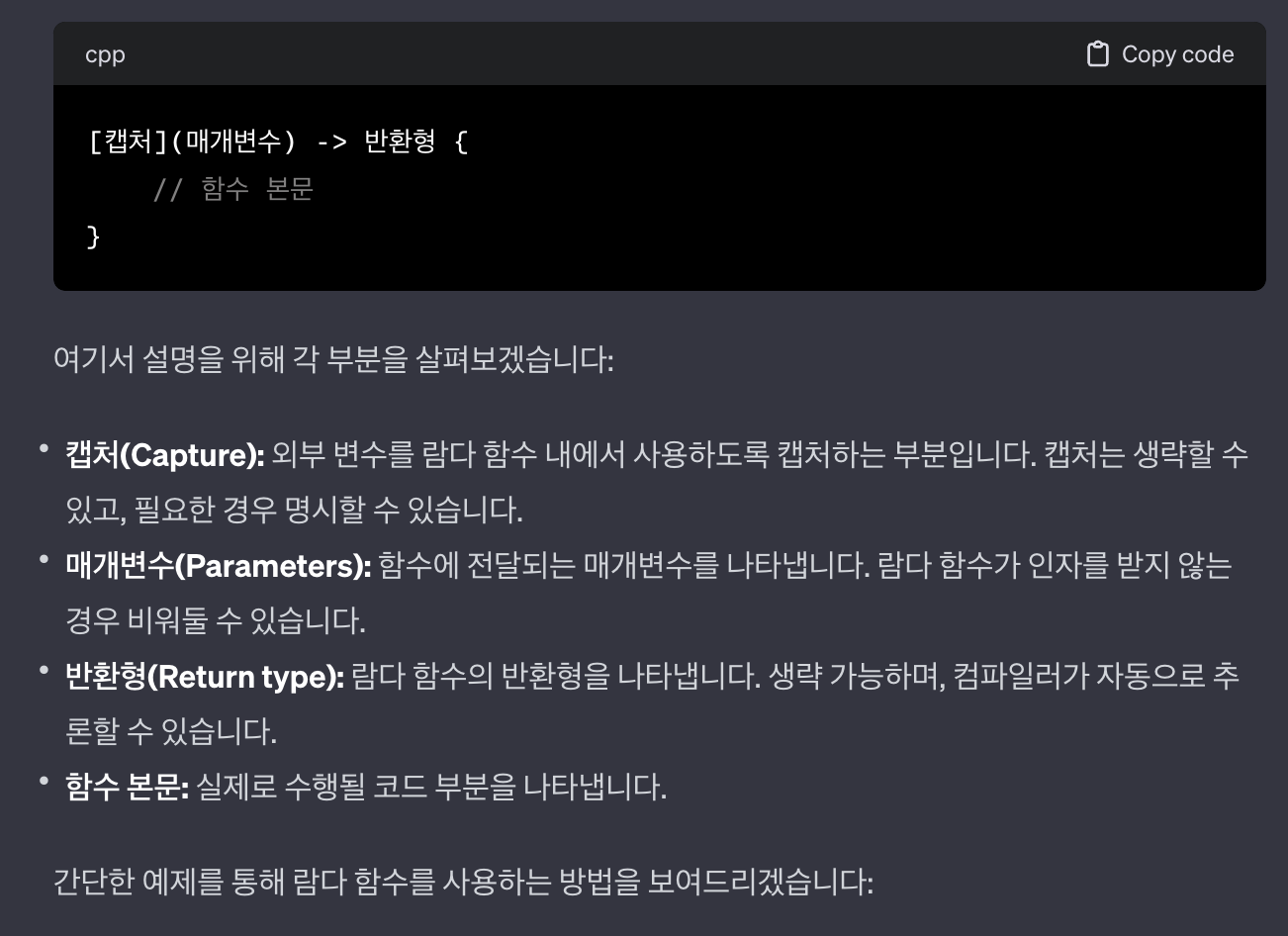
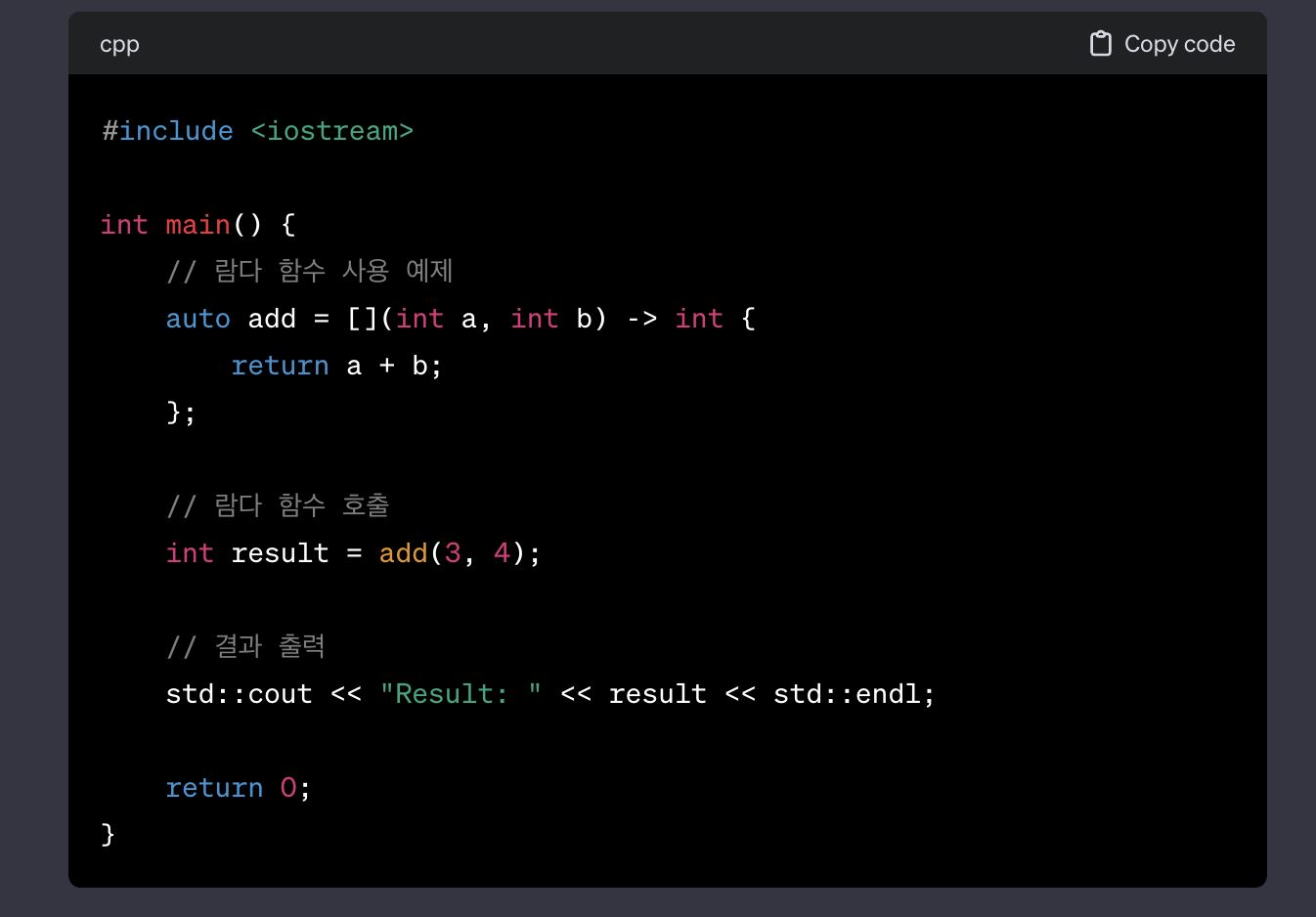
람다함수 사용법:
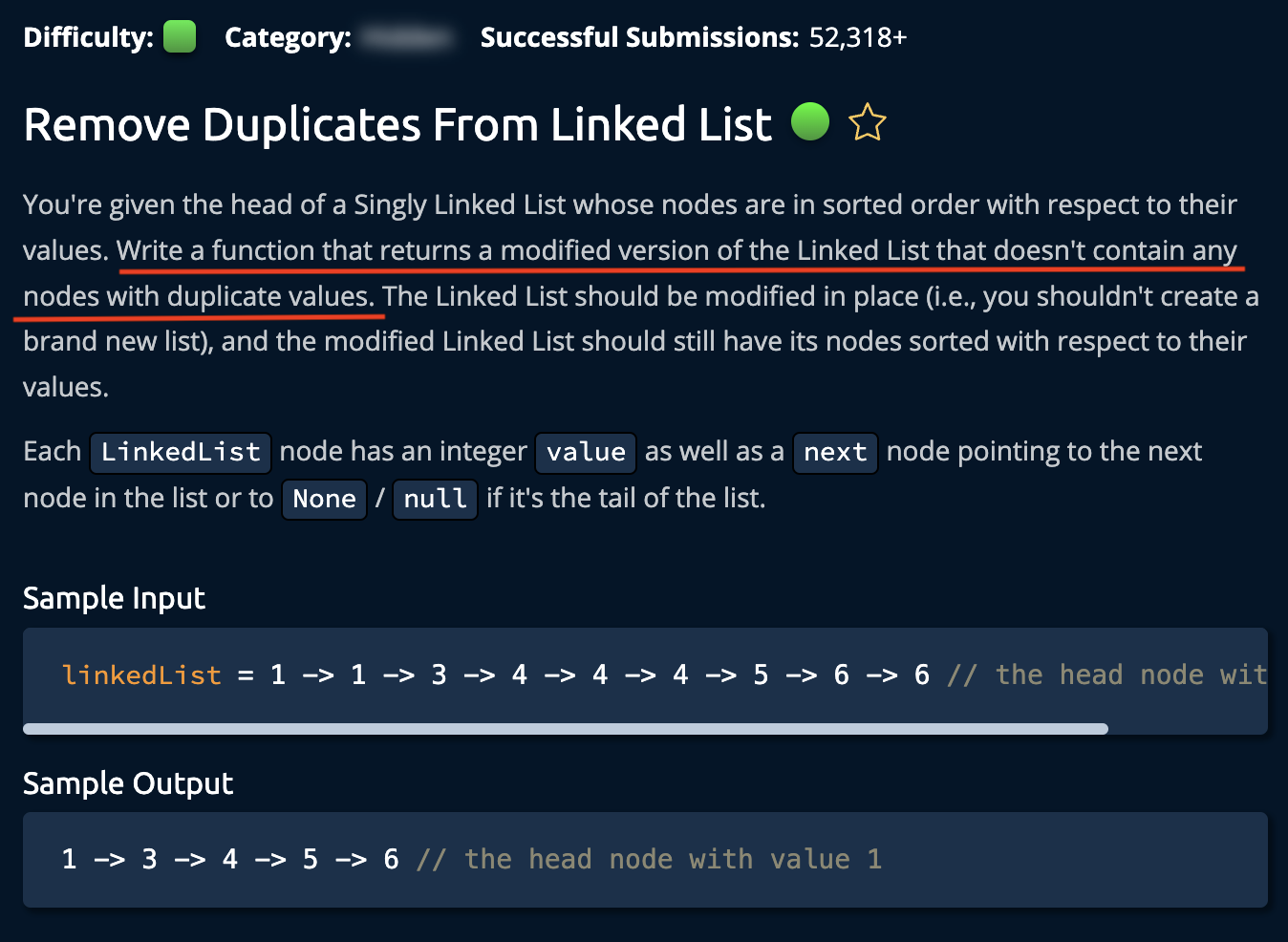
16. Remove Duplicates From Linked List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
// This is an input struct. Do not edit.
class LinkedList {
public:
int value;
LinkedList* next = nullptr;
LinkedList(int value) { this->value = value; }
};
LinkedList* removeDuplicatesFromLinkedList(LinkedList* linkedList) {
// Write your code here.
LinkedList* input = linkedList;
LinkedList* dummy;
// int i = 0;
while (linkedList->next != nullptr){
// cout << i++ << endl;
if (linkedList->value == linkedList->next->value){
dummy = linkedList->next;
linkedList->next = linkedList->next->next;
delete(dummy);
}
else {
linkedList = linkedList->next;
}
}
return input;
}
- 한줄요약: next 노드의 Value가 같으면, next 노드는 delete하고, 그 다음 노드 (linkedList->next->next) 가리키는 포인터를 그 다음 노드에 연결하면 끝.
17. Middle Node

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
// This is an input struct. Do not edit.
class LinkedList {
public:
int value;
LinkedList* next = nullptr;
LinkedList(int value) { this->value = value; }
};
LinkedList* middleNode(LinkedList* linkedList) {
// Write your code here.
LinkedList* traverse = linkedList;
int counter = 0;
int forward;
if (!linkedList->next) return linkedList;
while(traverse->next){
traverse = traverse->next;
counter++;
}
forward = (counter%2) ? counter/2+1 : counter/2;
for (int i=0; i< forward; i++){
linkedList = linkedList->next;
}
return linkedList;
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 => 6step / 3back /3forw
// 1,2,3,4,5,6 => 5step / 2back / 3forw
- 한줄요약: forward traversing 하면서 node 갯수 count 하고, 그 반만큼 한번 더 앞으로.
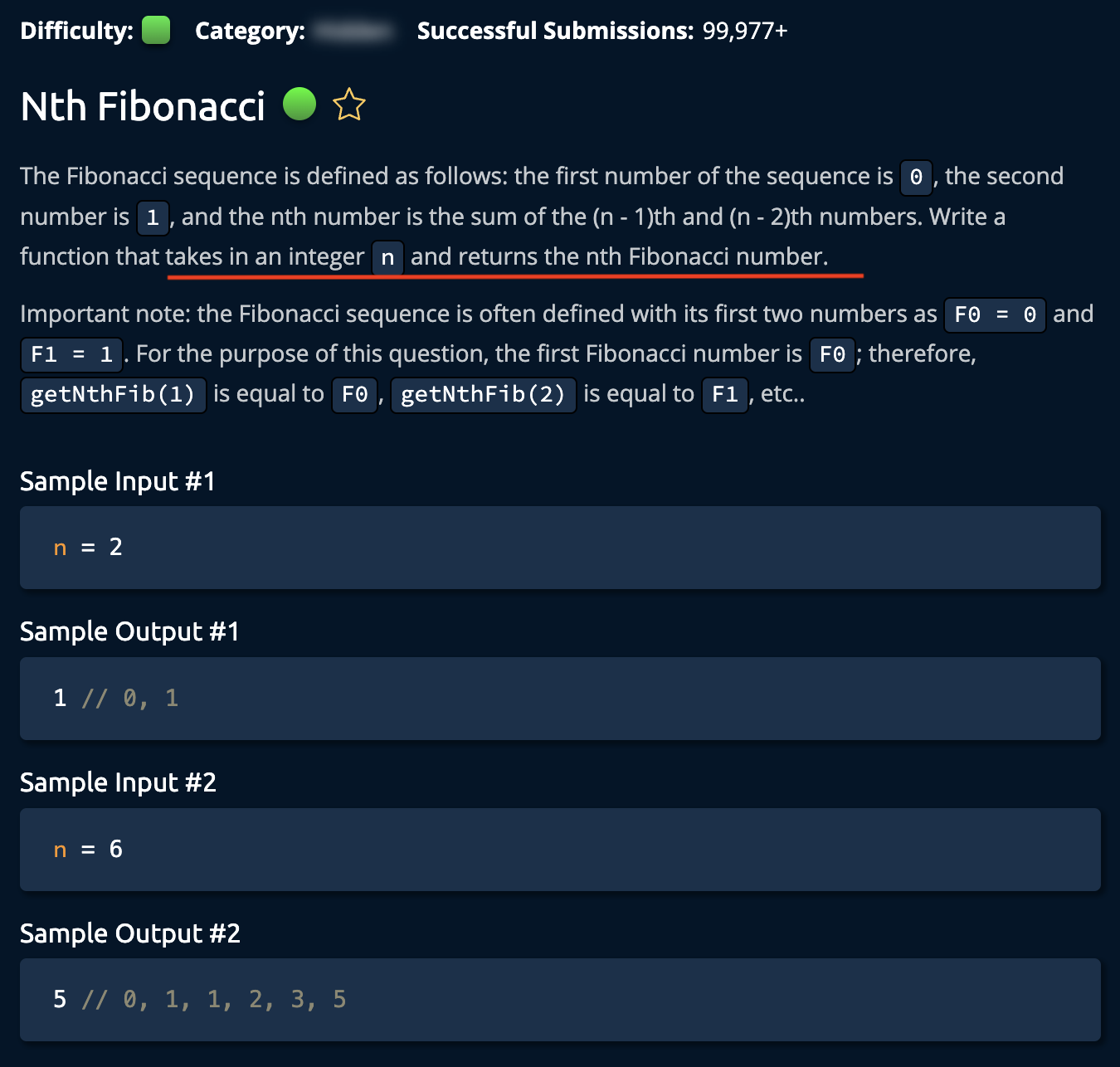
18. Nth Fibonacci
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
using namespace std;
int getNthFib(int n) {
// Write your code here.
int result = (n==0)? 0 : (
(n==1)? 0 : (
(n==2)? 1 : (
getNthFib(n-1)+getNthFib(n-2)
)));
return result;
}
- 한줄요약: 피보나치 수열의 recurrence formula만 정확히 써주면 자동으로 recursion 됨
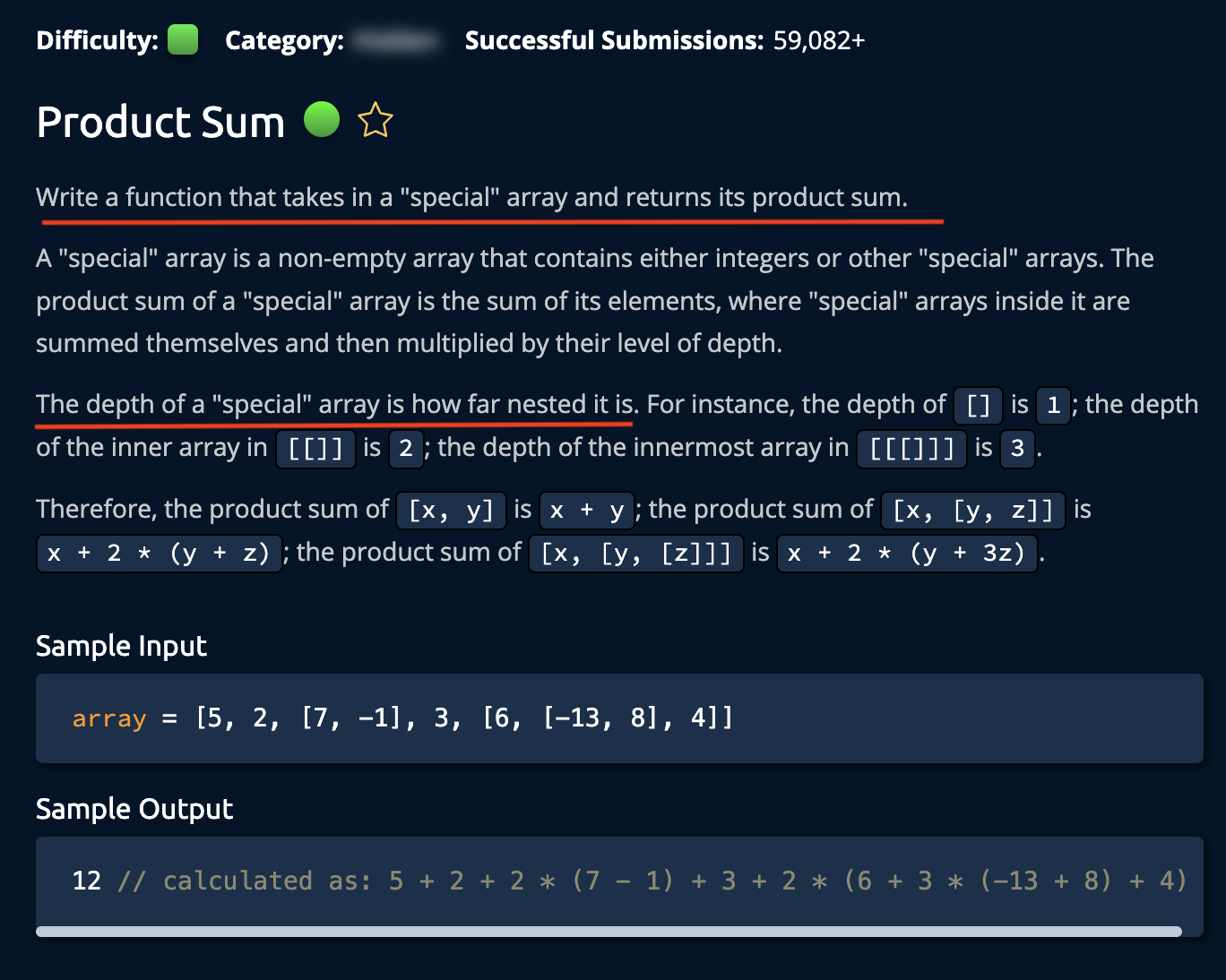
19. Product Sum
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
#include <any>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Tip: You can use el.type() == typeid(vector<any>) to check whether an item is
// a list or an integer.
// If you know an element of the array is vector<any> you can cast it using:
// any_cast<vector<any>>(element)
// If you know an element of the array is an int you can cast it using:
// any_cast<int>(element)
int depth = 1;
int productSum(vector<any> array) {
// Write your code here.
int sum = 0;
for (auto &element : array){
if(element.type()==typeid(vector<any>)){
depth++;
sum += productSum(any_cast<vector<any>>(element))*depth;
depth--;
}
else{
sum += any_cast<int>(element);
}
}
return sum;
}
- 한줄요약: nested vector인 array 벡터의 원소는 int 또는 nested vector 둘 중의 하나라서, producSum함수에서 (1) int면 sum에 숫자 더하고, (2) nested vector면 productSum 을 재귀호출하고, 결과값에 nest 된 만큼 depth를 곱해서, sum에 더하면 됨.
20. Binary Search

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(vector<int> array, int target) {
// Write your code here.
int vsize = array.size();
int Lp = 0;
int Rp = vsize-1;
while(true){
cout << "Lp:" << Lp << " Rp:" << Rp << endl;
if (array[Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2] == target){
cout << Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2 << endl;
return Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2;
}
if (Lp == Rp) {cout << "failed" << endl; return -1;}
if (array[Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2] > target){
Rp = Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2;
}
else{
Lp = Lp+(Rp-Lp)/2+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
- 한줄요약: binary search 하면 됨. 중간값 찾아서 target과 비교, 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽으로 가기.