Problems in LeetCode Beginner’s Guide
2235. Add Two Integers
Given two integers
num1andnum2, return the sum of the two integers.
1
2
3
4
class Solution:
def sum(self, num1: int, num2: int) -> int:
return num1 + num2
1
2
3
4
5
6
class Solution {
public:
int sum(int num1, int num2) {
return num1+num2;
}
};
2236. Root Equals Sum of Children
You are given the
rootof a binary tree that consists of exactly3nodes: the root, its left child, and its right child.Return
trueif the value of the root is equal to the sum of the values of its two children, orfalseotherwise.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def checkTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
return root.val == (root.left.val + root.right.val)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool checkTree(TreeNode* root) {
int sum = root->left->val + root->right->val;
if ( root->val == sum ) return true;
return false;
}
};
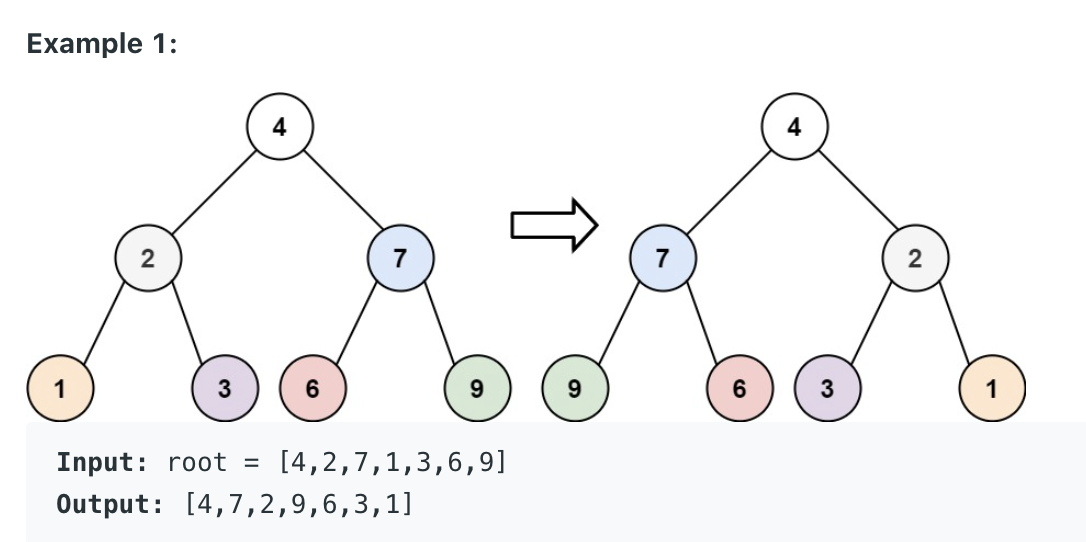
226. Invert Binary Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def switch_node(self, node):
tempNode = node.left
node.left = node.right
node.right = tempNode
return node
def recursiveInversion(self, node):
if node == None:
return node
elif (node.left None) and (node.right None):
return node
node = self.switch_node(node)
node.left = self.recursiveInversion(node.left)
node.right = self.recursiveInversion(node.right)
return node
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root);
TreeNode* switch_node(TreeNode* node);
TreeNode* recursive_inversion(TreeNode* node);
};
TreeNode* Solution::switch_node(TreeNode* node){
TreeNode* tempNode;
tempNode = node->left;
node->left = node->right;
node->right = tempNode;
return node;
}
TreeNode* Solution::recursive_inversion(TreeNode* node){
if (node == NULL){
return node;
}
node = switch_node(node);
node->left = recursive_inversion(node->left);
node->right = recursive_inversion(node->right);
return node;
}
TreeNode* Solution::invertTree(TreeNode* root){
root = recursive_inversion(root);
return root;
}
1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
Given an array
nums. We define a running sum of an array asrunningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i]).Return the running sum of
nums.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
result = []
accsum = 0
for num in nums:
accsum += num
result += [accsum]
return result
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> runningSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> result;
int accsum = 0;
// 7ms
//for (int i=0; i < nums.size(); i++){
// accsum += nums[i];
// result.push_back(accsum);
//}
// 4ms
for (int num : nums){
accsum += num;
result.push_back(accsum);
}
return result;
}
};
1672. Richest Customer Wealth
You are given an
m x ninteger gridaccountswhereaccounts[i][j]is the amount of money thei-thcustomer has in thej-thbank. Return _the wealth that the richest customer has.A customer’s wealth is the amount of money they have in all their bank accounts. The richest customer is the customer that has the maximum wealth.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Solution:
def maximumWealth(self, accounts: List[List[int]]) -> int:
max_money = 0
for customer in accounts:
customers_money = 0
for money in customer:
customers_money += money
if max_money < customers_money:
max_money = customers_money
return max_money
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class Solution {
public:
int maximumWealth(vector<vector<int>>& accounts) {
int maxWealthSoFar = 0;
for (vector<int> account : accounts){
int customer = 0;
for (int money : account){
customer += money;
}
maxWealthSoFar = max(maxWealthSoFar,customer);
}
return maxWealthSoFar;
}
};
412. Fizz Buzz
Given an integer
n, return a string arrayanswer(1-indexed) where:
answer[i] == "FizzBuzz"ifiis divisible by3and5.answer[i] == "Fizz"ifiis divisible by3.answer[i] == "Buzz"ifiis divisible by5.answer[i] == i(as a string) if none of the above conditions are true.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution(object):
def fizzBuzz(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[str]
"""
result = []
for j in range(n):
i = j+1
if (i%30) and (i%50):
result += ["FizzBuzz"]
elif (i%3==0):
result += ["Fizz"]
elif (i%5==0):
result += ["Buzz"]
else:
result += [str(i)]
return result
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> fizzBuzz(int n) {
vector<string> answer;
string FB;
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if ((i%30) && (i%50)) FB = "FizzBuzz";
else if (i%3==0) FB = "Fizz";
else if (i%5==0) FB = "Buzz";
else FB = to_string(i);
answer.push_back(FB);
}
return answer;
}
};
1342. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero
Given an integer
num, return the number of steps to reduce it to zero.In one step, if the current number is even, you have to divide it by
2, otherwise, you have to subtract1from it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
class Solution:
def numberOfSteps(self, num: int) -> int:
if (num == 0): return 0
if (not (num % 2)):
return 1 + self.numberOfSteps(num / 2)
else:
return 1 + self.numberOfSteps(num - 1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution {
public:
int numberOfSteps(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 0;
if (!(num % 2)){
return 1+numberOfSteps(num/2);
}
else {
return 1+numberOfSteps(num-1);
}
}
};
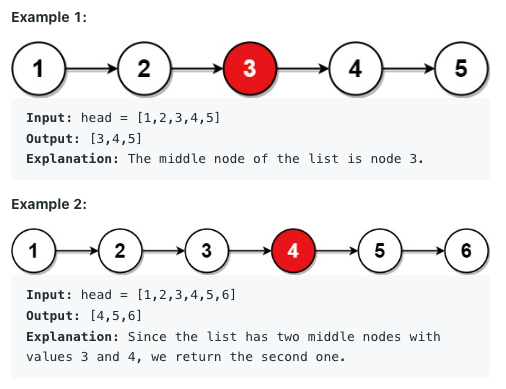
876. Middle of the Linked List
Given the
headof a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
arr = [head]
while arr[-1].next:
arr.append(arr[-1].next)
return arr[len(arr) // 2]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
vector<ListNode*> A = {head};
while (A.back()->next != NULL)
A.push_back(A.back()->next);
return A[A.size() / 2];
}
};
383. Ransom Note
Given two strings
ransomNoteandmagazine, returntrueifransomNotecan be constructed by using the letters frommagazineandfalseotherwise.Each letter in
magazinecan only be used once inransomNote.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution:
def canConstruct(self, ransomNote: str, magazine: str) -> bool:
# Check for obvious fail case.
if len(ransomNote) > len(magazine): return False
# In Python, we can use the Counter class. It does all the work that the
# makeCountsMap(...) function in our pseudocode did!
magazine_counts = collections.Counter(magazine)
ransom_note_counts = collections.Counter(ransomNote)
print(magazine_counts)
# For each *unique* character in the ransom note:
for char, count in ransom_note_counts.items():
# Check that the count of char in the magazine is equal
# or higher than the count in the ransom note.
magazine_count = magazine_counts[char]
if magazine_count < count:
return False
# If we got this far, we can successfully build the note.
return True
Reference
Notes Mentioning This Note
Table of Contents
- Problems in LeetCode Beginner’s Guide
- 2235. Add Two Integers
- 2236. Root Equals Sum of Children
- 226. Invert Binary Tree
- 1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
- 1672. Richest Customer Wealth
- 412. Fizz Buzz
- 1342. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero
- 876. Middle of the Linked List
- 383. Ransom Note
- Reference